Point cloud classification
The Point Cloud Classification tool allows the user to apply different parametric classifiers to point cloud data in order to prepare it e.g. for DEM product generation.
Valid inputs to the Point Cloud Classification tool are:
LiDAR takes available in a HxMap Project and
Infocloud data which has been processed and is available as a Point Cloud Filter job result
Select data from the project as described above for processing and go to ‘Tools’ > ‘Run Point Cloud Classification’.
Correct ground classification depends on precise georeferencing of the point cloud. For point cloud from LiDAR, run LiDAR Matching before classification. For point cloud from Infocloud, run Triangulation before generating Infocloud.
Class to Class Classification
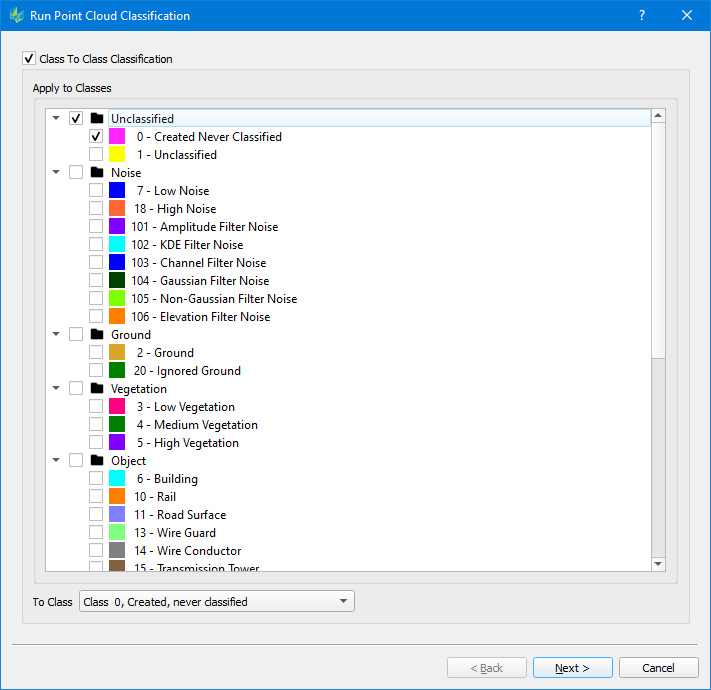 | Apply to Classes: the source classes which will be reassigned to a new class To Class: the target class to assign |
Polygon Classification
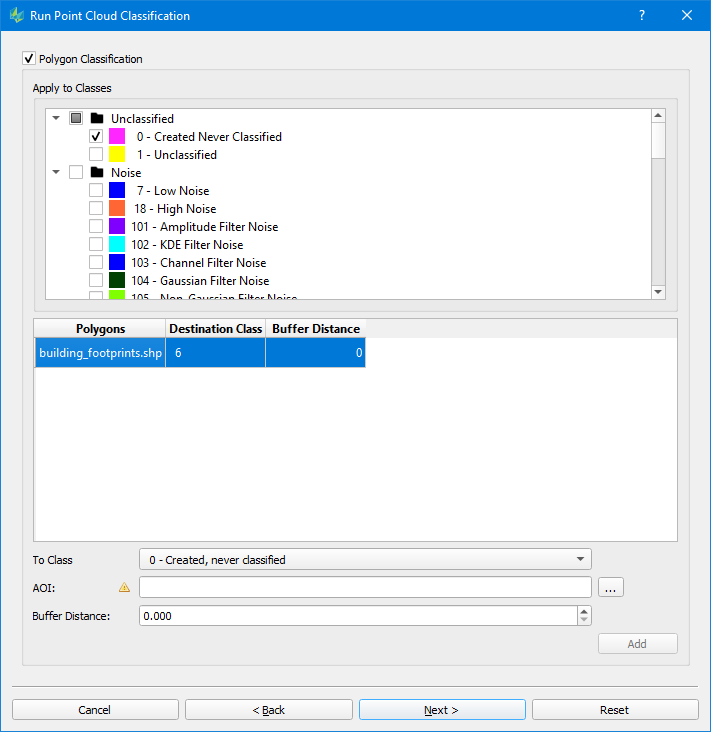 | Apply to Classes: the source classes which will be reassigned to a new class To Class: the target class to assign AOI: file containing the polygons to be used. Points from Apply to Classes which intersect the polygon in 2D (horizontal) space will be assigned to the To Class. Multiple polygon layers may be configured in a single classification run Buffer Distance: buffer to apply to polygons Polygons on different layers should not overlap each other, otherwise the classifier may give unexpected results for the Destination class of intersecting points. |
Ground Classification
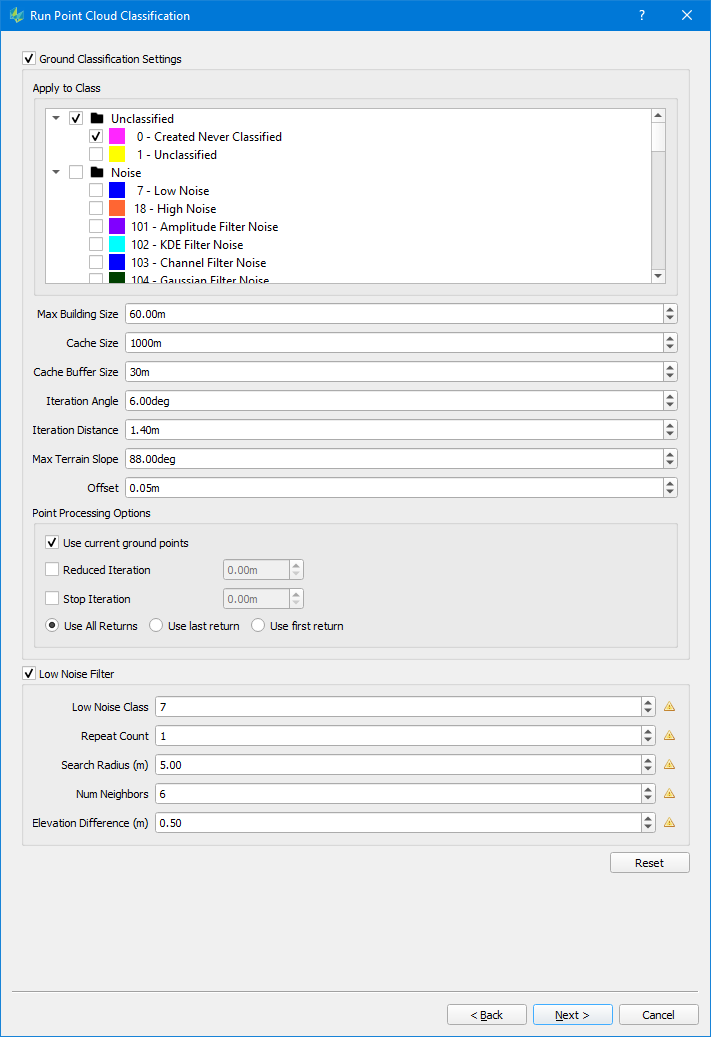 | Apply to Classes: the source classes which will be reassigned to the Ground Class (class 2) Max Building size (m): maximum side length of a building in the input data The max building should be larger than the max diagonal length of the largest building in the area so that the classifier does not mistakenly choose the building points as ground seed points, which eventually causes parts of the large building to be classified as the ground. For dense vegetation and rugged terrain area, you may lower the max building size. It can help to select more ground seed points and will help to get more details of the true terrain model Iteration angle (degrees) and Iteration distance (m):
If so, this point is added to the ground class. This parameter is critical to classify different terrain types. For rugged terrain, increase the iteration angle. This will help to approximate the high relief terrain better, but most likely may also classify some low vegetation points mistakenly. To avoid low vegetation in such scenarios, it is recommended to decrease the iteration distance alongside. Max Terrain Slope (degrees): max. allowed slope angle in TIN, will be used to avoid high slope triangles Offset: Vertical offset to classify the points close to ground surface to ground points in the final iteration Point Processing Options Use current ground points: if enabled, already existing ground points (e.g. from a previous classification) are used as key points to identify additional ground points Reduced iteration: If enabled, the refinement of the triangles will be less aggressive. Once the max. triangle length of a given triangle is below the given distance specified via the “Reduced Iteration” setting, the iteration angle will be reduced proportional for further iterations. Stop iteration: If enabled, the refinement of triangles will stop, as soon the max. triangle length of a given triangle is below the iteration threshold Options “Reduced Iteration“ & “Stop Iteration“ may be used like a Thinning tool when dealing with quite dense point clouds Use all/ last/ first return: specify the type of returns to be used in the classification process. (Default = all) |
Global Cache Settings
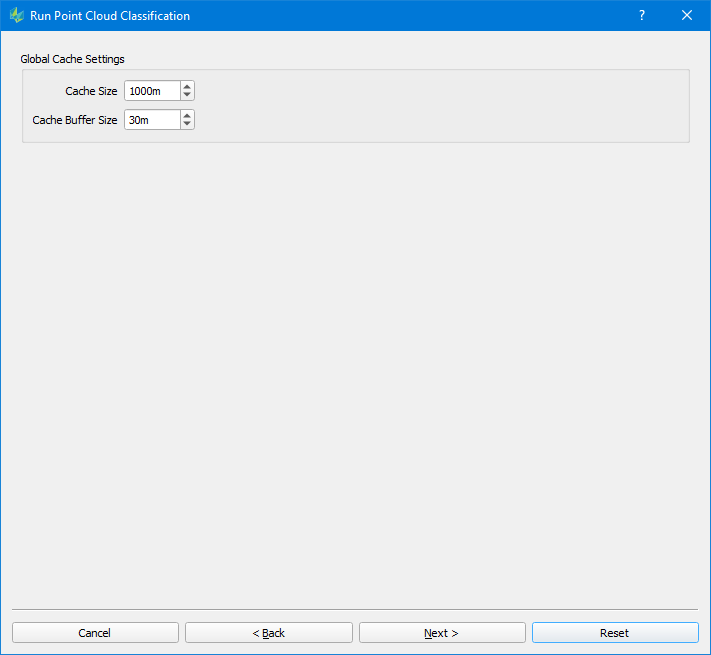 | Cache Size: the size of the tile to be processed in meters. Each tile will be processed as one unit in memory. The memory required for a tile is a function of the cache size and the point density of the input point cloud. Cache size may need to be reduced if there is not enough memory available. Cache Buffer Size: when Ground Classification is applied set to one-half the building size parameter used. Otherwise a value of 50 meters will serve for most cases. |